Guide: The term "Triode" suggests a device with three electrodes. But what exactly is a triode, and how does it work? Let’s explore together!
1. The Working Principle of Triode – Introduction
A triode, also known as a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), is a current-controlled semiconductor device used to amplify weak signals into stronger electrical signals. It can also function as a switch without any physical contact. The triode consists of two closely spaced PN junctions on a single semiconductor substrate. These junctions divide the semiconductor into three regions: the emitter, the base, and the collector. Depending on the doping type, the structure can be either PNP or NPN. As one of the core components in electronic circuits, the triode enables current amplification and plays a crucial role in various applications.
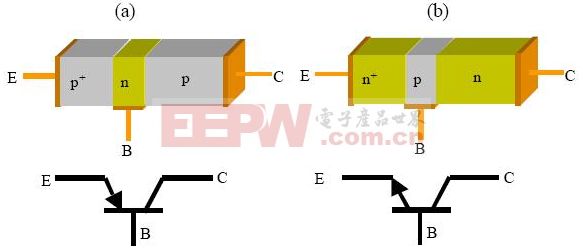
2. Triode Working Principle – Structure
The basic structure of a triode consists of two reverse-biased PN junctions, forming either a PNP or NPN configuration. The three terminals are called the emitter (E), base (B), and collector (C), each with a specific role during operation. The emitter is typically marked with an arrow in circuit diagrams, indicating its direction of current flow. In the absence of external bias, the PN junctions form a depletion region that separates the p-type and n-type materials. This setup is fundamental to how the triode controls and amplifies current.
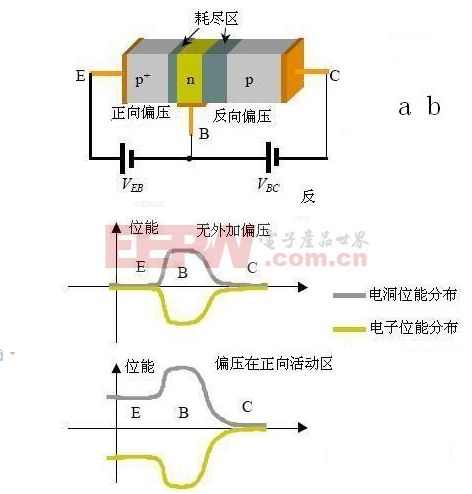
3. The Working Principle of Triode
Consider a PNP transistor in the active region, as shown in Figure (a). When forward-biased, the depletion region at the emitter-base junction narrows, allowing holes from the emitter to flow into the base. At the same time, electrons from the base move toward the emitter. On the other hand, the base-collector junction remains reverse-biased, creating a wide depletion region that prevents direct conduction. However, when a voltage is applied, the injected holes from the emitter diffuse through the base and reach the collector junction, where they are swept by the electric field into the collector. This process results in a large collector current, enabling signal amplification.
For further reading:
- How a Triode Clamp Works
- Basic Knowledge and Working Principle of Triode
- Understanding How a Triode Operates
- Phone Battery and Electronic Components
XT Series (15 - 23.6 Inch )
XT Series Infrared Touch Screens (15" - 23.6") – High-Performance Multi-Touch Solutions
Key Features:
-
- Infrared Touch Technology: No physical contact required for touch detection, minimizing wear and tear while ensuring long-term reliability.
- High Transparency & Clarity: Anti-glare, anti-reflective, and optically bonded options available for superior display visibility.
- Robust Durability: Resistant to scratches, moisture, and dust, making it ideal for high-traffic public and industrial use.
- True Multi-Touch Support: Supports 10-point Touch for advanced gestures (pinch, zoom, swipe) and multi-user interaction.
- Wide Compatibility: Works seamlessly with Windows, Android, Linux, and macOS, supporting plug-and-play USB or RS-232 connectivity.
- Customization Options: Choice of open-frame, in-glass bonding, or standalone touch overlays to fit various display integrations.
- High Sensitivity & Response Speed: <5ms touch response time for fluid, lag-free operation.
- Water & Dust Resistance: IP65-rated options available for harsh environments.
Applications:
-
- Self-service kiosks (ticketing, retail, ATMs)
- Interactive digital signage & wayfinding
- Education & digital whiteboards
- Industrial HMI & control panels
- Gaming & entertainment displays
interactive touch screen,tempered infrared IR touch screen,small size infrared touch screen
Guangdong ZhiPing Touch Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.zhipingtouch.com