Guide: The term "Triode" suggests a device with three terminals. But what exactly is a triode, and how does it work? Let's explore together!
1. Working Principle of the Triode – Introduction
A triode, also known as a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), is a current-controlled semiconductor device that amplifies weak electrical signals into stronger ones. It can also function as a solid-state switch without any mechanical components. The triode consists of two closely spaced PN junctions on a single semiconductor material, dividing it into three regions: the emitter, base, and collector. These are arranged in either PNP or NPN configurations. As one of the most fundamental components in electronic circuits, the triode enables signal amplification and switching functions.
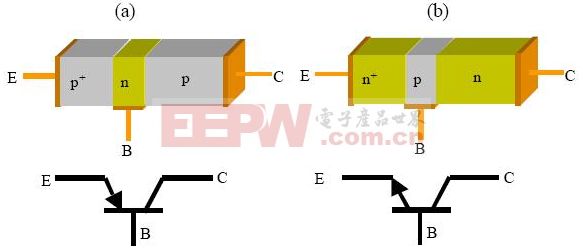
2. Triode Working Principle – Structure
The basic structure of a triode comprises two reverse-biased PN junctions, forming either a PNP or NPN configuration. The three terminals are called the emitter (E), base (B), and collector (C). Their names reflect their roles during operation. The emitter is usually marked with an arrow in circuit diagrams, indicating the direction of current flow. In a normal state, without any external voltage, the PN junctions create a depletion region that separates the p-type and n-type materials. This setup is crucial for the triode’s ability to control current flow.
3. The Working Principle of the Triode
Let’s look at a PNP transistor in the active region. When forward biased, the emitter-base (EB) junction narrows its depletion region, allowing holes from the emitter to enter the base. At the same time, electrons from the base move toward the emitter. Meanwhile, the collector-base (CB) junction is reverse biased, creating a wider depletion region that prevents direct current flow. However, once the holes from the emitter reach the CB junction, they are swept into the collector by the electric field, creating a significant current. This is the core mechanism behind the triode’s amplification capability.
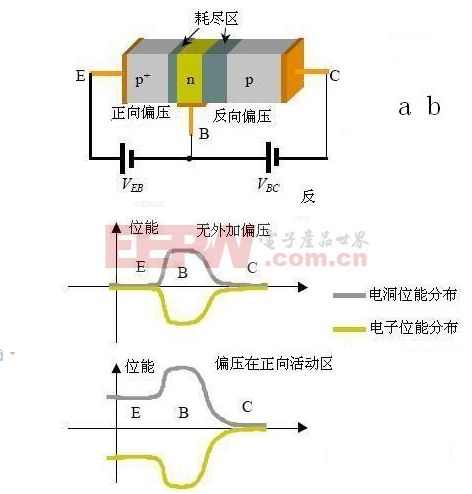
Understanding how a triode works helps in grasping the fundamentals of modern electronics. Unlike two separate diodes, the close proximity of the junctions in a triode allows for efficient current control and amplification. This makes it an essential component in amplifiers, switches, and various other electronic applications.
Further Reading:
- How a Triode Clamp Works
- Basic Knowledge and Working Principle of a Triode
- How Does a Triode Function?
- Understanding Smartphone Battery Systems
industrial computer,pc fanless,small industrial pc
Guangdong ZhiPing Touch Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.zhipingtouch.com