Guide: Amplifier  As the name suggests, it is a device used for amplification. The following small series will introduce you to the amplifier.
As the name suggests, it is a device used for amplification. The following small series will introduce you to the amplifier.  The principle, children's shoes come to learn how it is magnified ~~~
The principle, children's shoes come to learn how it is magnified ~~~
Amplifier  Principle -- Introduction
Principle -- Introduction
Amplifier  is a device that increases the amplitude or power of a signal. It consists of tubes, transistors, and other components. Amplifiers are essential in automation and signal processing systems. Amplifier
is a device that increases the amplitude or power of a signal. It consists of tubes, transistors, and other components. Amplifiers are essential in automation and signal processing systems. Amplifier  works by using an input signal to control an energy source, with the energy supply providing the necessary power for amplification. Linear amplifiers
works by using an input signal to control an energy source, with the energy supply providing the necessary power for amplification. Linear amplifiers  reproduce and enhance the input signal, while non-linear amplifiers
reproduce and enhance the input signal, while non-linear amplifiers  produce outputs based on a functional relationship with the input.
produce outputs based on a functional relationship with the input.

2. Amplifier  Principle - Power Amplifier
Principle - Power Amplifier 
High-frequency power amplifier  is a device that converts DC energy into high-frequency AC output. It is used in the final stage of transmitters to amplify modulated signals. Amplifier
is a device that converts DC energy into high-frequency AC output. It is used in the final stage of transmitters to amplify modulated signals. Amplifier  can be classified into three working states: A, B, and C, with most operating in Class C.
can be classified into three working states: A, B, and C, with most operating in Class C.
Class A amplifier  has a current flow angle of 360 degrees and is suitable for low-power signal amplification.
has a current flow angle of 360 degrees and is suitable for low-power signal amplification.

The output stage of a power amplifier  uses a large static current to ensure both halves of the signal are amplified linearly. If the signal is too strong, distortion may occur due to saturation or cutoff.
uses a large static current to ensure both halves of the signal are amplified linearly. If the signal is too strong, distortion may occur due to saturation or cutoff.
Class B amplifier  has a current flow angle of about 180 degrees. It uses two transistors to amplify each half of the signal, which reduces distortion but can cause crossover distortion if not properly biased.
has a current flow angle of about 180 degrees. It uses two transistors to amplify each half of the signal, which reduces distortion but can cause crossover distortion if not properly biased.

Class AB amplifier  has a current flow angle between 180 and 360 degrees. A small bias current is added to reduce crossover distortion, making it more efficient than Class A.
has a current flow angle between 180 and 360 degrees. A small bias current is added to reduce crossover distortion, making it more efficient than Class A.

Class C amplifier  has a current flow angle less than 180 degrees. It is commonly used in RF applications where a tuned circuit filters out distortion, resulting in a clean output waveform.
has a current flow angle less than 180 degrees. It is commonly used in RF applications where a tuned circuit filters out distortion, resulting in a clean output waveform.

3. Amplifier  Principle - Operational Amplifier
Principle - Operational Amplifier 
An operational amplifier (op-amp) has two inputs: the inverting (-) and non-inverting (+), and one output. It amplifies the difference between the two input voltages. Op-amps are widely used in audio, filtering, and signal conditioning circuits.
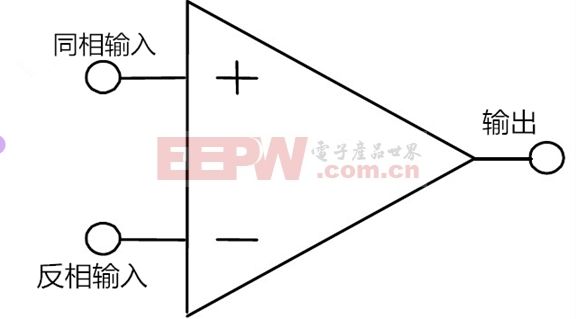
If the voltage at the inverting terminal is higher than the common ground, the output voltage will be opposite in direction. Conversely, if the non-inverting terminal is higher, the output follows the same direction. This makes op-amps versatile for various configurations like inverting and non-inverting amplifiers.

Operational amplifier  output is proportional to the difference between the two inputs. In audio systems, the formula is often expressed as: Output Voltage = A₀ × (E₠- E₂), where A₀ is the open-loop gain, and E₠and E₂ are the input voltages at the non-inverting and inverting terminals, respectively.
output is proportional to the difference between the two inputs. In audio systems, the formula is often expressed as: Output Voltage = A₀ × (E₠- E₂), where A₀ is the open-loop gain, and E₠and E₂ are the input voltages at the non-inverting and inverting terminals, respectively.
Expand reading:
1. In-depth understanding of the differential amplifier 
2. These operational amplifiers  Did you notice the knowledge?
Did you notice the knowledge?
3. Various amplifiers  Comparison
Comparison
Electronic tube
modular rj45 jack,rj45 connector,rj45 jack,cat6a rj45,rj11 connector,rj11 jack,rj11 4p4c,rj11 modular jack
Dongguan Yiyou Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.dsubminiature.com