 The LCD liquid crystal display is an abbreviation of Liquid Crystal Display. The LCD is constructed by placing a liquid crystal cell among two parallel glass substrates, and a TFT (thin film transistor) is disposed on the lower substrate glass. A color filter is disposed on the upper substrate glass and passes through the TFT. The signal and voltage changes to control the direction of rotation of the liquid crystal molecules, so as to achieve the purpose of controlling whether or not the polarized light of each pixel is emitted or not. Now that LCD has replaced the CRT as the mainstream, the price has dropped a lot and it has been fully popularized.
The LCD liquid crystal display is an abbreviation of Liquid Crystal Display. The LCD is constructed by placing a liquid crystal cell among two parallel glass substrates, and a TFT (thin film transistor) is disposed on the lower substrate glass. A color filter is disposed on the upper substrate glass and passes through the TFT. The signal and voltage changes to control the direction of rotation of the liquid crystal molecules, so as to achieve the purpose of controlling whether or not the polarized light of each pixel is emitted or not. Now that LCD has replaced the CRT as the mainstream, the price has dropped a lot and it has been fully popularized. The liquid crystal itself does not emit light and can only produce a color change, requiring the backlight source to see the displayed content. Traditional notebook screens use cold cathode fluorescent tubes (CCFLs) as backlights, and LED backlights use LEDs, which is the difference between the two.
The white LED is a point light source, and the CCFL tube is a strip light source. Small white LEDs use DC power supplies, which can be used in series and in multiple applications. However, for a few watts or more, appropriate drive circuits must be considered to increase efficiency. CCFL tube must have "high pressure plate" supporting use.
There are several LCD backlight modes, including LED and CCFL or CCFT.
The CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) backlight is currently the most important backlight product for LCD TVs. Its working principle is that when high voltage is applied to both ends of the lamp, a small number of electrons in the lamp will impact the electrode at high speed to generate secondary electron emission and begin to discharge. After the mercury or inert gas in the tube is impacted by electrons, it excites radiation at 253.7 nm. The UV light generated by the UV light excites the phosphor coated on the inner wall of the tube to generate visible light.
CCFL lamp life is generally defined as: In the ambient temperature of 25 °C, with the rated current to drive the lamp, the brightness is reduced to the initial brightness of 50% of the working time length of the lamp life. At present, the nominal life of LCD TV backlight can reach 60000 hours. The CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) backlight is characterized by low cost, but the color performance is inferior to the LED backlight.
LED backlight uses light-emitting diodes as a backlight source, which is the most promising alternative to traditional cold cathode fluorescent tubes. Light-emitting diodes are made of several layers of thin, doped semiconductor materials, one layer with an excessive amount of electrons, and the other layer lacking electrons to form positively charged holes. Current passes through during operation, and electrons and holes combine with each other. The energy is released in the form of light radiation. By using different semiconductor materials, light emitting diodes having different light emitting characteristics can be obtained.
Light-emitting diodes that have been put into commercial use can provide colors such as red, green, blue, cyan, orange, amber, and white. The main use of mobile phone is white LED backlight, and the LED backlight light source used in LCD TV can be white, it can also be red, green, blue three primary colors, in the high-end products can also be applied multi-color LED backlight to further improve color Expressive, such as six primary color LED backlight light source.
The advantage of using LED backlight is that the thickness is thinner, about 5 centimeters, and the color gamut is also very wide. It can reach 105% of the NTSC color gamut. The black luminous flux can be reduced to 0.05 lumens, and the contrast ratio of the LCD TV can reach 10000:1. . At the same time, the LED backlight source also has a lifetime of 100,000 hours. At present, the problems that restrict the development of LED backlights are mainly cost. Because the price is much higher than that of the cold fluorescent lamp light sources, LED backlight light sources can only appear in high-end LCD TVs abroad.
LED backlight light source advantages
1. The screen can be made thinner. We pay attention to some LCD monitors. We can see that there are several filament-shaped CCFL lamps. In order to make the screen evenly luminous, we need to add some other devices, so we can't do it very much. Thin; and the backlight is different, LED backlight itself is a planar light-emitting material, without adding other devices.
2. The picture is better CCFL backlight screen is generally the middle brightness and the surrounding is not the same, while the screen is all black when some of the white 3. Will not be yellow and dark CCFL fluorescent lamps and fluorescent lamps, a long time will be aging, so the traditional After two or three years, the notebook screen will turn yellow and dark, and the life of the LED-backlit screen will be much longer, at least two or three times.
4. More power saving Everyone knows that fluorescent lamps are required to bombard mercury vapor at a very high voltage, so the power consumption of CCFL screens is large, and the power consumption of a 14-inch screen is generally more than 20 watts. LED is a kind of semiconductor, works under the low pressure, the structure is simple, the power consumption is small, especially good for the notebook's endurance ability.
5. The more environmental protection CCFL light mercury has a great deal of pollution to the environment, and there are great difficulties in harmless recycling.
How CCFL Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps Work
The physical structure of the CCFL cold cathode fluorescent tube is that a neon gas Ne+Ar mixed gas is sealed in a glass tube, which contains a trace amount of mercury vapor (several mg), and a phosphor is coated on the inner wall of the glass. The CCFL cold cathode fluorescent lamp passes the electrodes at both ends of the lamp tube and causes the ultraviolet rays excited by the gaseous mercury in the lamp tube to collide with the phosphor on the tube wall, thereby emitting light. Its wavelength is determined by the characteristics of the phosphor material.
CCFL cold cathode fluorescent tube defects
Currently, CCFL light sources commonly used in LCD TVs are very similar to those used in our day-to-day fluorescent tubes, both in terms of light-emitting principle and physical structure. The light source has the advantages of simple structure, small temperature rise on the surface of the lamp tube, high brightness on the surface of the lamp tube, and easy processing into various shapes. However, the service life is short, mercury is contained, and the color gamut is narrow. It can only reach 70% to 80% of NTSC. For large-size TV screens, CCFL's voltage boost and lengthening of the tube processing are also difficult.
First, the most vexing problem is the short service life. The service life of CCFL backlight is generally 15000 hours to 25000 hours. The longer the LCD is used (especially the LCD screen of the notebook computer), the longer the brightness declines. After 2 to 3 years of use, the LCD screen will be dark and yellow. This is the result of the shorter service life of CCFLs.
Second, the use of liquid crystal displays is limited. Each pixel in the liquid crystal display is composed of three rectangular blocks of R, G, and B, and the color performance of the liquid crystal display depends entirely on the performance of the backlight module and the color filter. The three primary colors of the color filter film are the same as the white light emitted by the CCFL. The CCFL backlight module does not actually meet the design requirements and can only reach about 70% of the NTSC standard.
Third, the structure is complex and the brightness output uniformity is poor. Since the cold cathode fluorescent lamp is not a planar light source, in order to realize a uniform luminance output of the backlight, the backlight module of the LCD needs to be matched with a plurality of auxiliary devices such as a diffusion sheet, a light guide plate, a reflective plate, etc., but the screen is displayed when the entire white or black screen is displayed. The difference in brightness between the edges and the center is very obvious.
Fourth, the larger size, power consumption is not ideal. Since CCFL backlights must include complex optics such as diffusers and reflectors, the volume of the LCD cannot be further reduced. In terms of power consumption, LCDs using CCFLs as their backlights are also unsatisfactory, and CCFL backlights for 14-inch LCDs often consume 20 W or more.
Of course, in the last two years, domestic and foreign manufacturers have made some improvements to the drawbacks of traditional CCFLs. They all seem to have reached a very high standard. Manufacturers' propaganda is even more impressive. However, these improvements are limited and cannot completely eliminate CCFL backlights. Congenital technical defects.
From the current situation of the backlight or CCFL tube, the cost may be slightly lower and the technology is relatively mature. LED backlighting is still limited to mobile phones, MP3, MP4 and other small screen products. For large screen products, it is still a direction of efforts. However, it is more advantageous to save power.
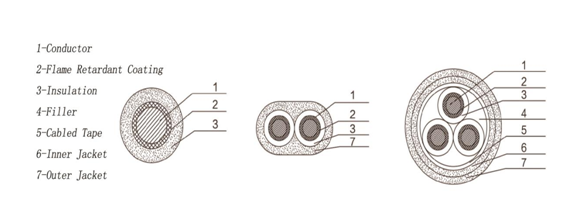
Mineral Insulated cables, or simply Mica cables, are cables in which
conductors or wires are enclosed by a metal jacket and insulated with
hard-packed mica. It is a variety of electrical cable made from copper
conductors inside a copper sheath, insulated by mineral mica powder. Mineral
Insulated cable is a specialized type of cable used in high temperatures
or harsh environmental conditions because it has low flammability, even
when operating at high temperatures. The maximum continuous operating temperature is
250℃. The cable can supply with power continuously for 3 hours
at 950-1000℃. The mineral fillings in cables provide excellent non-reactive
insulation. It resists oxidation and enables precise measurement.

Advantages:
- Low flammability
- Resists oxidation
- Easy installation
- Long service life
- High insulation resistance
- High mechanical strength
- Excellent shield performance
- Exceptional vibration resistance to protect the mechanical conditions of the internal conductor wires
- Can be drawn down to extremely small diameters, providing fast response times when used in temperature sensors
- Can be formed/bent in the field without causing short circuits between the sheath and the internal wires, or between wires
- Can be easily sealed around when used as extension or control cables in critical environments
Application:
- Nuclear or hydrocarbon based energy plants
- Emergency power systems
- Exposure to dangerous gasses
- Emergency lighting systems
- Public buildings such as theatres, cinemas, hotels
- Hospital operating rooms
- Fire alarm systems
- Transport hubs (railway stations, airports etc.)
- Tunnels and mines
- Electrical equipment in hazardous areas
- And many more...

Welcome to visit our factory to learn more about us. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
Mineral Insulated Cable,Fire Resistance Mica Cables,Highly Fireproof Power Cables,Metallic Sheathed Power Cables
Fujian Lien Technology Co.,Ltd , http://www.liencable.com