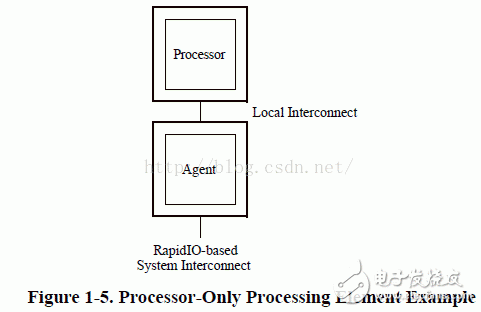
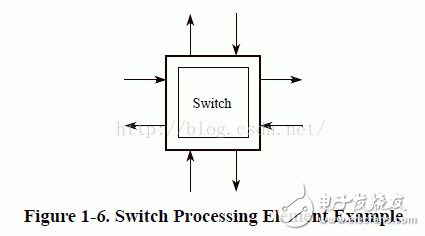
2.1 System Model
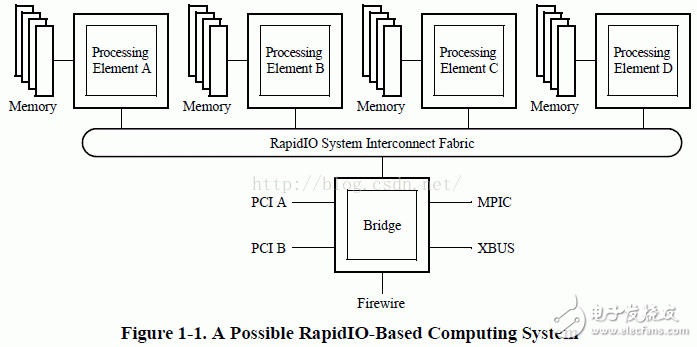
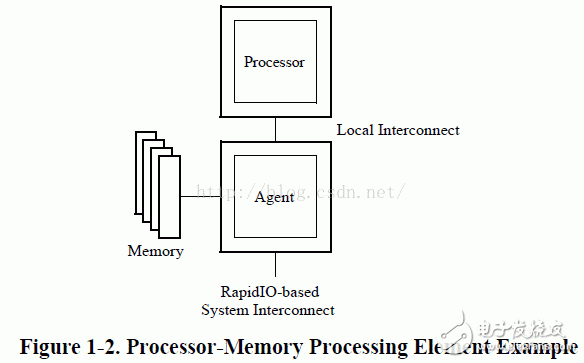
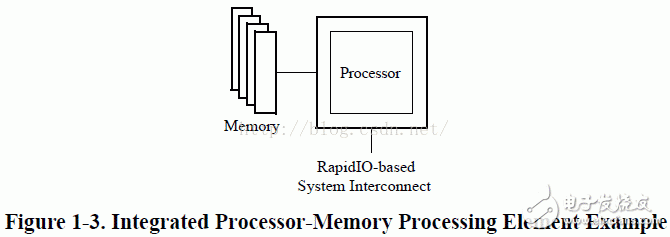
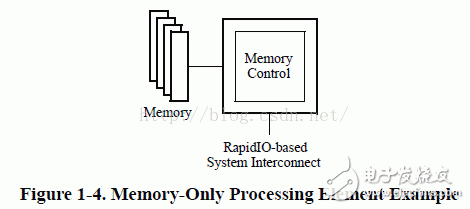
This chapter outlines the various device units that can be part of a RapidIO-based system. The RapidIO protocol is designed to support a wide range of devices, each playing a specific role in enabling high-speed communication between components. Understanding these units is essential for designing and implementing efficient systems based on RapidIO technology.

In the e-bike market where innovative, minimalistic designs are talk of the day, we see that manufacturers are constantly looking for smart electrical wiring systems and reliable connections to support these developments. With years of experience with our e-bike customers, we have already worked successfully around themes like the integration of brake & signal, battery and number plate lighting, high power electrical connection.
Related products:bike wire assembly, ebikes connector,e-bike cable assemblies, waterproof e-bike cable, waterproof e-bike connector
bike wire assembly, ebikes connector,e-bike cable assemblies, waterproof e-bike cable, waterproof e-bike connector
ETOP WIREHARNESS LIMITED , https://www.etopwireharness.com