introduction
This article refers to the address: http://
With the rapid development of high technology such as computer technology, digital processing and image compression technology, traditional TV has entered a new era of digital TV. (Digital TV - refers to a TV system that is fully digitalized from the production, production, editing, storage, transmission, transmission, to signal reception, processing, display, etc.)
With the full digitization of TV broadcasting and the development of Internet technology, digital TV signals can be received not only by the "set-top box + TV set" mode, but also directly on a PC.
This paper expounds and analyzes the practical significance and development trend of receiving digital TV signals by PC, and gives an implementation scheme of a digital TV receiving system based on PC.
1. Major foreign technical standards and the status quo of digital TV standardization in China
1.1 Foreign Digital TV Technology Standards
At present, there are three main standards for digital TV in the world [1]:
1) DVB (Digital Video Broadcasting) of European ETSI;
DVB encodes digital video, audio and multimedia data signals into MPEG-2 video, audio and multimedia signals that are multiplexed into source output signals. They can be fed separately to the DVB-S/C/T channel. Three members of the DVB family:
1. DVB-S for satellite digital TV broadcasting
The characteristics of the satellite channel are: available frequency bandwidth, limited power, large interference, and low signal to noise ratio. Therefore, a highly reliable signal modulation method is required, and a strong signal error correction capability is required, and the bandwidth requirement is not particularly high. Therefore, DVB-S adopts forward error correction (FEC) (including Viterbi coding, interleaving, RS coding and scrambling circuits), and quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) modulation channel processing, and then transmits to the satellite link; The opposite process is performed upon reception. The DVB-S standard has been recognized worldwide.
2. DVB-C for wired (coaxial cable) digital TV broadcasting
Wired channels are characterized by high signal-to-noise ratio, narrow band resources, echoes and nonlinear distortion. This requires DVB-C to adopt a modulation scheme with narrow bandwidth, high frequency band utilization, and strong anti-interference ability. At the same time, due to the high channel signal-to-noise ratio and low bit error rate, the error correction capability is not very high. Therefore, the channel part of DVB-C adopts RS code, convolutional code interleaving and quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) technology. DVB-C is accepted in Europe, Australia, North America, South America and Other countries.
3. DVB-T for terrestrial digital TV broadcasting
The characteristics of terrestrial broadcasting are: complex terrain, time-varying fading and multipath interference, low signal-to-noise, and support for mobile reception. Therefore, DVB-T uses forward error correction (FEC) (including inner code interleaving, inner code Viterbi coding, outer code interleaving, outer code RS coding) and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (COFDM) which can effectively eliminate multipath interference. And Gray code mapping 4/16/64QAM modulation and other techniques for channel processing. The digital television program is then transmitted in the 6 MHz, 7 MHz, and 8 MHz bands originally used for the simulation. The bit rate of DVB-T transmission is variable. Digital TV terrestrial broadcasting DVB-T has been extensively tested and approved in Europe, Australia and Singapore [2].
2) Japan's DiBEG ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting), derived from DVB;
3) DTV of the Advanced Television System Committee (ATSC).
ATSC's DTV is a terrestrial digital TV broadcasting standard that competes with DVB-T and has been tested in comparison with DVB-T in countries such as Australia and Singapore. The countries and regions currently accepting the standard include the United States, Canada, Mexico, Argentina, South Korea, and Taiwan. In addition, North America accepts DVB-S and DSS (Housass Digital Satellite System) standards for satellite digital TV broadcasting; OpenCable (Digital Cable Standard developed by CableLabs of the United States) for cable digital TV broadcasting, which accepts ATSC and International Telecommunications Union (ITU) ITU-TJ83 cable digital multi-program format for television, voice and data services). The ATSC system consists of three subsystems: source coding and compression, service multiplexing and transmission, and radio/transmission. Source encoding and compression can be used for video, audio and auxiliary data, respectively. In HDTV systems, video encoding uses the MPEG-2 video stream syntax and audio encoding uses the Dolby AC-3 digital audio compression standard. The Service Multiplexing and Transport subsystem packs and multiplexes video, audio, and auxiliary data from their respective data stream packets into a single data stream using the MPEG-2 transport stream syntax. Interoperability between various digital media and computer interfaces is fully considered in the transmission. The RF/Transmission Subsystem completes channel coding and modulation. Reception is the inverse of the transmission [3].
1.2 Status Quo of Digital TV Standardization in China
In 1999, China began to implement the specialization of digital TV industrialization. In the second year, the National Digital TV Standards Committee was established, and the formulation of China's digital TV standards was officially launched. The Ministry of Information Industry and the State Administration of Radio, Film and Television have also set up a special expert group for standardization to carry out the collation and research of digital TV standards at home and abroad.
At present, in the digital TV ground standard scheme, the two most popular factions are DMB-T (“Northernâ€) with multi-carrier modulation technology led by Tsinghua University, and single carrier with Shanghai Jiaotong University as the core. Modulation technology ADTB-T ("Southern"). Since November 2004, both Tsinghua and Shanghai Jiaotong University have conducted ground-transmitting experiments and have achieved success. What is even more exciting is that on January 22, 2005, China’s first “Zhongshi No.1†digital TV terrestrial transmission chip with complete independent intellectual property rights based on TMB-T system of Tsinghua University came out at Fudan University. It is a major breakthrough in the independent design and manufacturing technology of China's digital TV million-gate ASIC. In September 2006, the technical standards for digital terrestrial wireless transmission in China have been adopted and will be formally implemented in the coming year.
2. The significance and development trend of receiving digital TV signals with PC
2.1 The significance of receiving digital TV signals with a PC
Personal computers (PCs) play an important role in the development of digital television. Huge usage (more than 350 million units), open technical standards and low cost. The use of PC to achieve digital TV reception is more interactive and random than the "set-top box + TV" receiving mode. Users can watch the programs they want to watch without restriction according to their own preferences. The PC's monitor has megapixel resolution and is fully capable of displaying high definition television (HDTV) images. In addition, the cost of developing HDTV on a PC platform is also quite low. The reception of digital television through a PC is cheaper and more practical than purchasing an expensive digital television receiver separately, making it more attractive to consumers.
In addition, because the computer network uses the TCP/IP protocol, users can easily combine TV services with Internet browsing, email, and a variety of online consulting, entertainment, education, and business functions.
2.2 Development trend
After several years of research on digital TV in China, it has achieved considerable development and won the full support of the state and policy. At present, relevant departments have set a time period for the development of digital TV: 2008 Digital Olympics, 2015 deadline.
Many users now use analog TV cards to watch TV shows on a PC. This shows that the combination of TV and PC has a considerable market share. In the past few years, the PC-based analog TV receiving card market has developed steadily. Thanks to its rich visual experience and interactive data value-added services, DTVPC cards are becoming a more attractive solution than today's PC analog TV receiver cards. When the "cinema" entertainment project is combined with the real-time interactivity of the PC, the look and feel of digital TV is considerably enhanced compared to analog TV. A potential user who buys an analog TV card will be more willing to invest more money in a synthetic board that supports both analog and digital TV to avoid the "set-top box + analog TV" that will soon be eliminated. risk. Moreover, consumers can try to experience the high-definition TV on a PC monitor before considering spending a lot of money to add a high-definition TV to the room. The radio and television company has a certain foundation in the installation and use of DTVPC cards, and is also confident to produce more digital TV program content, which will promote the development of the digital TV industry in general.
In recent years, Internet TV (IPTV) has developed rapidly. As a new medium, it covers five major media such as radio, television, newspapers, the Internet, and telecommunications networks. It is a combination of information technology, network technology, and computer technology. At present, the development of digital TV and Internet TV in China has begun to enter a fast track, and the government is stepping up efforts. It can be said that the relationship between traditional digital TV and the current Internet TV is correctly handled, the copyright of Internet TV and the interests of all parties are solved, so that users can see high-quality digital TV programs on their own PCs. It is a problem that needs to be solved in the industry and the future development trend of the industry.
3. PC-based digital TV receiving system (DTVPC)
3.1 DTVPC Solution
DTVPC solutions must meet the following requirements in order to be widely accepted by consumers:
· A single board solution can simultaneously receive the actual HDTV and traditional analog TV reception;
· Simple and convenient installation;
· prices that can be accepted by the mass consumer market;
· Support PC screen display format.
Digital TV receiver cards must also support multi-level sync monitors and normal PC display resolutions such as 1024 x 768, 800 x 600 and 640 x 480. If the board supports DVD playback in addition to ATSC and NTSC programs, its use value for consumers will be greatly improved.
FIG. 1 is a technical solution of a DTVPC card based on a PCI interface. This receiver card has 16MB of SDRAM memory for supporting the actual HDTV display format (up to 720P and 1080I). The DTV card is connected to the graphics subsystem via an analog loopback cable, which introduces the RGB video data and horizontal and vertical sync signals of the graphics card into the receiving card. The analog switch is selected in the DTVPC and graphics card. The DTVPC decoder can be programmed to control this analog switch. When the video output of the decoder is selected, the HDTV broadcast program can be displayed full screen on the screen of the PC regardless of the introduced video format.
This scheme also allows display in the form of a video window on the graphical desktop. The decoder can simultaneously output high definition analog video compatible with CCIR 601 digital video. The CCIR 601 video data is sent to the video capture port of the graphics card through the video interface port (VIP) of the PCI bus. The graphics card overwrites the transmitted video data into a video window at the top of the display graphic, and the viewer can select the full-screen HDTV. Input mode, you can also watch digital TV programs from a video window while doing other work on the PC.
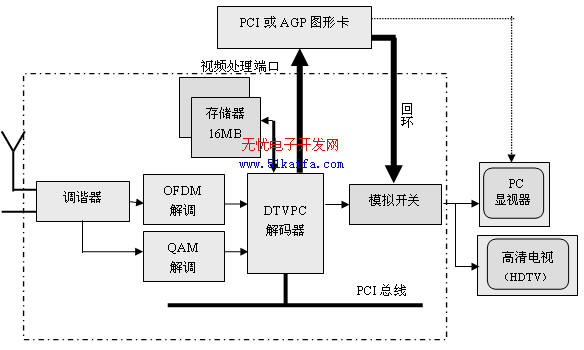
Figure 1 DTVPC solution
3.2 Basic functions of the DTVPC solution
All the advantages currently in the "set top box + TV" mode can be implemented under the DTVPC solution. The main features of this program are:
· Multicast reception: It is especially useful when sending multiple sets of programs on the same TV station. Viewers will have the opportunity to choose the program they want to watch or watch all the programs at the same time.
• Record/playback: This function is the same as that of a VCR or recorder, using a PC's hard drive to allow viewers to save content that may be received for later viewing.
Pause/time shift: This feature differs from a VCR or recorder in that the viewer has the opportunity to pause while the live broadcast is in progress and then start over.
· Data Broadcasting: From a technical point of view, digital TV broadcasting is just a series of simple continuous data streams. It can send pictures, sounds, multimedia games and other content related to the TV programs you watch, making the viewer's experience more personalized. Turn.
· Interactive TV: Real-time interactivity allows viewers to purchase music CDs while participating in MTV broadcasts, or to compete in game programming [4].
DTVPC cards will be an ideal building block in the interactive TV market. This is because most PCs already have the most important function necessary to implement interactive television - a mechanism to provide feedback to viewers. Most PCs are now connected to the Internet, allowing viewers to send control information such as on-demand to service providers at any time.
3.3 Technical Features of DTVPC Solution
At the heart of the DTVPC solution is the decoder. There are three basic methods for implementing decoders: software decoding, hardware decoding, and hardware assist + software decoding.
1. Software decoding transfers all processing work to the CPU of the PC. This method has a heavy CPU load and requires high CPU performance. A PIII750MHz CPU plus a high-performance graphics chip can only decode the 480P digital TV stream. If the HDTV format is decoded by software, only the decoding part requires CPU up to 1GHz.
2. Hardware decoding uses a dedicated DTV decoder chip. This solution does not rely on the CPU or graphics chip to complete the decoding of the DTV stream. The CPU bandwidth consumption is very small and can be used on most PCs, but the board is used. higher cost.
3. This solution uses hardware-assisted + software decoding. It consists of three parts: a receiving card, a high-performance CPU and a graphics chip. The receiving card includes a digital television tuner and an 8-VSB demodulator, and is responsible for receiving the DTV broadcast signal and transmitting it to the CPU. The CPU separates the transmitted signals and decodes the digital television code stream using a software algorithm. The motion compensation circuitry and inverse cosine transform (IDCT) logic integrated in the graphics chip can help the CPU do some of the work. This solution has a good compromise between CPU performance and board cost. A PIII 550 MHz CPU and a high-performance graphics chip can decode the 1080I format digital TV stream.
4. Conclusion
Based on the status quo of digital TV technology and the technical characteristics and technical requirements of DTVPC system, this paper proposes a preliminary scheme of DTVPC system based on the current technical level, and uses hardware-assisted plus software decoding method to make PC CPU performance. There is a good compromise between requirements and board costs. However, because the technology of the DTVPC system is still evolving, whether the solution can be put into commercial use remains to be further improved and tested.
Piezoelectric Buzzer Element,Piezo Disc,Piezo Disc Manfacturer
SWT Smart Technology Co., Ltd. , http://www.fuding-sound.com